Withdrawal from alcohol, commonly known as the alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), is the unpleasant process your body goes through when you try to stop drinking alcohol or can’t consume alcohol for any reason (such as if it’s unavailable).
Alcohol depresses the Central Nervous System (CNS). When an individual drinks too much alcohol, their brain begins to develop a tolerance to its effects. Eventually, the person will feel that drinking is necessary to feel normal or to get through the day.
If you stop drinking suddenly, you may experience unpleasant and sometimes dangerous withdrawal symptoms. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) can cause severe physical changes in the body, making it challenging to manage alcohol use. It can also make it extremely difficult to lessen or stop alcohol abuse.
Importance of Alcohol Detox
The best way to overcome alcohol addiction is to stop using as soon as possible. When someone undergoes alcohol detox, they refrain from drinking on purpose so that their body can adapt to functioning without alcohol.
Alcohol detox requires a person to experience a spectrum of withdrawal symptoms, which may be unpleasant, upsetting, and even deadly. Withdrawal often leads to relapse, but detox provides the opportunity to stop drinking safely and less unpleasantly.
Since specific symptoms of alcohol withdrawal are harmful, detoxification from alcohol should be done under medical supervision at a rehab facility. Those who detox from alcohol with professional help are more likely to do it safely and effectively. A detox may not be pleasant, but it is a critical first step for alcoholics seeking recovery. A person in recovery might begin therapy in a treatment program after completing detox.
Symptoms of Alcohol Detox
During alcohol detox, withdrawal symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening. Often, the intensity and duration of your alcohol use disorder (AUD) will influence the withdrawal symptoms you encounter. For example, those with a history of excessive alcohol use are more prone to experience severe withdrawal symptoms.
Despite its rarity, delirium tremens (DTs) are the most severe side effect of alcohol withdrawal. It can begin anywhere between two and five days after the last drink and can be fatal. However, less than five percent of alcoholics will experience delirium tremens after they stop drinking.
A medical expert should supervise alcohol detox due to the severity of some withdrawal symptoms.
This is specifically true for those with a history of lung or heart disease or other medical disorders, as withdrawal symptoms can intensify quickly. Your treatment specialist will monitor your blood pressure and heart rate to ensure your condition does not worsen.
You may also discuss your symptoms with them and any discomfort you may be experiencing. This information helps your medical team identify which medication will ease your pain.
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline
The timing, duration, and severity of withdrawal symptoms depend on your situation. Although your symptoms may not follow this timeframe, withdrawal typically occurs in three phases for most people. The majority of patients recover within a week.
Within Six Hours
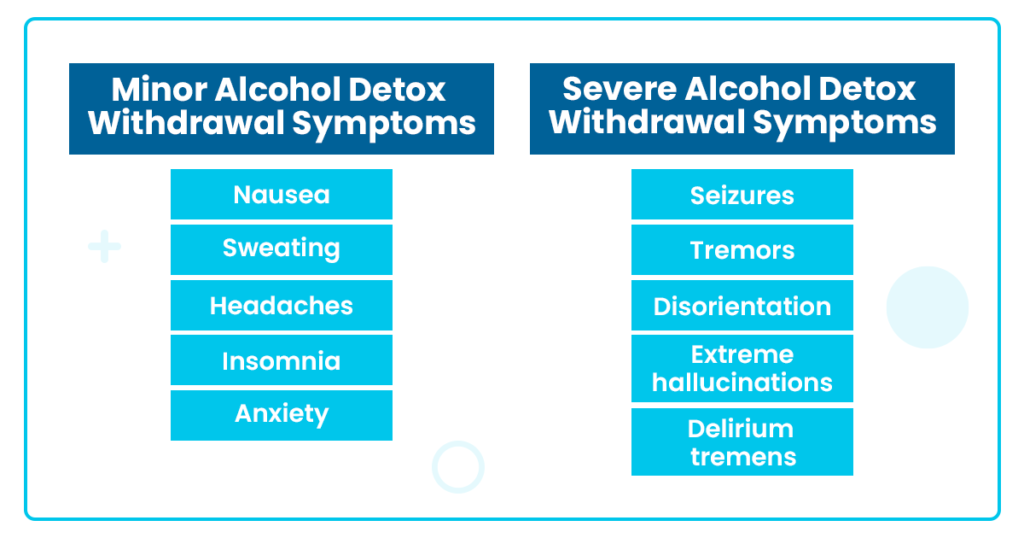
Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can occur as early as six hours after the last drink. Typically, the initial symptoms are discomforting but mild. They may consist of:
- Nausea
- Tremors
- Changes in your blood pressure
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
The majority of individuals recover from alcohol withdrawal after experiencing these symptoms.
Between 24 and 72 Hours
Severe symptoms, including seizures, manifest in the majority of alcoholics during the first 48 hours after their last drink. Over 5 percent of alcohol withdrawal sufferers will enter this phase and experience seizures.
Symptoms often reach their height between 24 and 72 hours after the previous drink. If, after 48 hours, you have not experienced significant symptoms such as seizures, you will likely recover. However, developing them in the future is still possible, so you should seek medical attention.
Between 48 to 72 Hours
Approximately 50 percent of those who experience withdrawal seizures will later develop DTs. Most individuals who develop DTs do so between 48 and 72 hours after their last drink. Therefore, the first several days after cessation are the most important and deadly during withdrawal. You must seek medical care during this time, particularly if you are exhibiting signs of DTs.
Weeks to Months
Some individuals experiencing alcohol withdrawal may experience symptoms for longer (from one week to several months) after quitting drinking. This is known as post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS). Post-acute withdrawal is characterized by persistent insomnia and mood disorders.
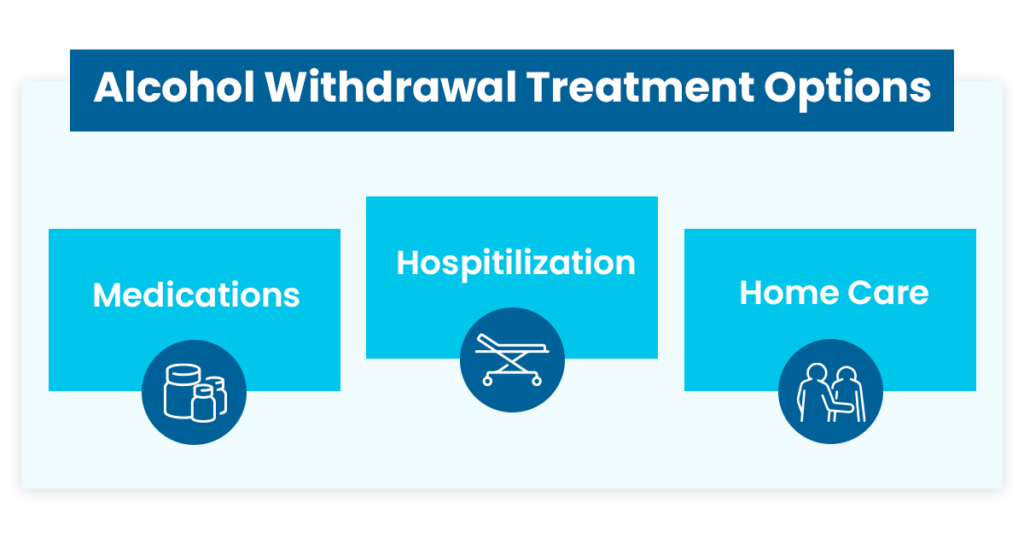
Treatment of Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome (AWS)
The treatment for AWS varies on the severity of the symptoms. Patients with mild symptoms can be treated at home, while others may require hospitalization to avoid potentially life-threatening health complications.
The primary objective of treatment is to maintain your comfort through symptom management. Your doctor’s treatment goal is to assist you in quitting drinking as fast and securely as feasible.
Home Care
Often, mild AWS symptoms can be managed at home. A family or relative must monitor your condition all the time. If your symptoms worsen, they must transport you to the hospital or call 911 immediately.
Additionally, they should ensure that you attend your counseling appointments and regularly contact your doctor for any routine blood tests that may be ordered. You may also require testing for alcohol-related health conditions.
If your home environment is not conducive to staying sober, consult your healthcare provider. Your doctor can help you connect with shelter programs for alcoholics in recovery.
Hospitalization
If your withdrawal symptoms are of severe nature, you may require hospitalization. Inpatient or outpatient treatment programs are necessary so that your doctor can monitor your condition and address any issues. You may need intravenous (IV) fluids to avoid dehydration and medications to alleviate your withdrawal symptoms.
Medications
AWS symptoms are often treated with benzodiazepines, which are sedatives. The most often prescribed benzodiazepine is chlordiazepoxide. Other benzodiazepines that doctors often prescribe are lorazepam (Ativan) and alprazolam (Xanax).
Benzodiazepines receive a boxed warning from the Food and Drug Administration due to the potential of developing dependency. If you are prescribed a medication from this class, discuss the risks with your doctor before taking it, and always follow the doctor’s instructions.
In addition, vitamin supplements may be used to replenish the essential vitamins depleted by alcohol consumption. Once the withdrawal is complete, taking further medications and nutritional supplements may be necessary to treat problems and dietary deficiencies caused by persistent alcohol use.
Is it Possible to Go Through Alcohol Withdrawal Safely?
It is 100 percent possible to complete alcohol withdrawal safely with the proper medical treatment. Various effective treatments are available to aid with alcohol withdrawal and recovery. Seeking treatment is always a safer option than attempting alcohol withdrawal on your own. A healthcare professional can determine if you can undergo withdrawal at home or if you need medical assistance. Always ask your doctor before attempting alcohol withdrawal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do you feel when you suddenly stop drinking?
If you are a heavy drinker, your body may initially revolt if you abstain from alcohol. You could experience cold chills, a rapid heartbeat, nausea, vomiting, trembling hands, and extreme anxiety. Some people even experience seizures or hallucinations. Your doctor can provide counseling and may prescribe medications such as benzodiazepines or carbamazepine to help you get through it.
How long does it take to get back to normal after stopping drinking?
Between 48 and 72 hours, the bulk of withdrawal symptoms will begin to lessen, allowing you to operate more normally and control your symptoms.
Does the body recover when you stop drinking?
When you quit drinking, your body has the opportunity to heal from alcohol’s adverse effects, but it may take some time before you feel like yourself again. If you plan to quit drinking, you should visit a doctor since alcohol withdrawal symptoms can be severe and lead to dangerous effects.
Let The Haven Detox Help You Live Sober Life
Those who drink excessively and those who have attempted self-detox in the past are at the most risk for complications during alcohol withdrawal.
Although attending a treatment program may frighten you, it is the safest approach to detox from alcohol. Friends and relatives can give emotional support, but they are not medically educated to know which alcohol withdrawal treatments are effective.
By enrolling in an alcohol addiction treatment program at The Haven Detox, you will get care from a team of medically qualified specialists who will assist you through the withdrawal process and lead you to recovery.
For additional information, contact us at (561) 328-8627 today!






