
Dr. Rostislav Ignatov, MD
Chief Medical Officer
Gabapentin is a prescription medication for treating nerve pain and seizures. In alcohol or drug detox, it is sometimes used “off-label,” to make withdrawal symptoms easier to handle.
Gabapentin is an optional support medication. It is not a core part of alcohol or drug detox protocols and does not replace critical medications like Suboxone for opioid cravings or benzodiazepines for preventing alcohol seizures and DT risk.
Table of Contents
Withdrawal symptoms often make the nervous system feel stuck on high alert. Gabapentin helps calm that overactivity, to:
| Reduce Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Like: | Reduce Opioid Withdrawal Symptoms Like: |
| Anxiety and feeling on edge | Anxiety and agitation |
| Trouble sleeping | Trouble sleeping |
| Shakiness and restlessness | Restless legs and body aches |
| Irritability | Nerve-type pain or sensitivity |
| Reduce Stimulant Withdrawal Symptoms Like: | Reduce Sedative / Benzo Withdrawal Symptoms Like: |
| Feeling “wired” or agitated | Anxiety/panic |
| Trouble sleeping (or flipped sleep schedule) | Trouble sleeping |
| Restlessness | Tremor and restlessness |
| Irritability | Irritability |
Gabapentin helps turn down how intensely nerve cells fire and talk to each other.
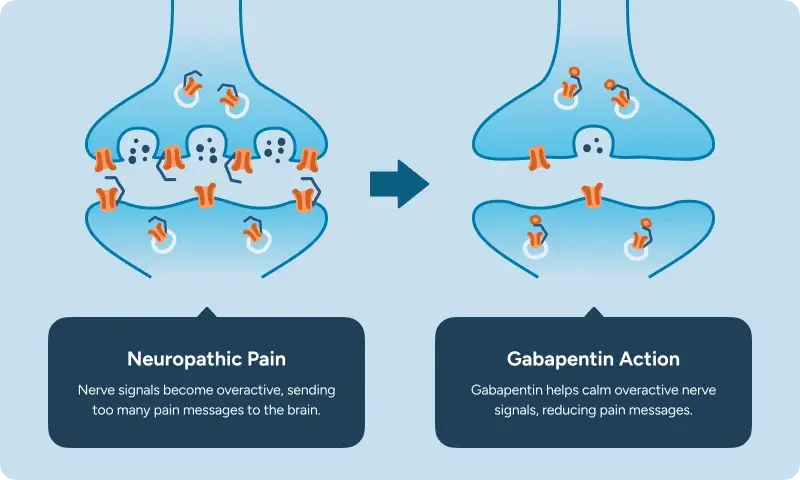
Even though gabapentin was made to resemble GABA (the brain’s main calming chemical), it does not attach to GABA receptors. The FDA label states the exact way gabapentin works is not fully understood, though this calcium-channel binding is well documented.
In detox, gabapentin is usually started to take the edge off symptoms not to “knock you out.” The goal is to help you feel calmer and more comfortable while staying alert and safe.
Gabapentin may be started on Day 1, though sometimes it’s safer to wait until the patient is more alert and stable.
Our general protocol is to:
Detox sometimes includes other meds that can also cause drowsiness (like sleep meds, certain anti-anxiety meds, or muscle relaxers). When medications “stack,” staff may space doses out or use lower amounts to keep breathing and alertness safe.
Most patients describe gabapentin as taking the edge off. You may feel less “wired,” less restless, and more able to settle down and sleep. It should not make you feel euphoric or out of control.
The goal is comfort and stability so you can think clearly and get through detox safely.
| What it should feel like | What it should not feel like |
| Calmer thoughts and less panic | “Nodding off” or being hard to wake up |
| Less restlessness or “crawling out of my skin” feeling | Dizziness so strong you can’t walk steadily |
| Fewer body aches or nerve-type discomfort | Confusion or feeling out of it |
| Easier time falling asleep |
For most patients gabapentin does not cause a “high.” If you feel unusually buzzed, confused, or too sleepy, tell the medical team right away. That usually means the dose is too strong or stacking with other medications.
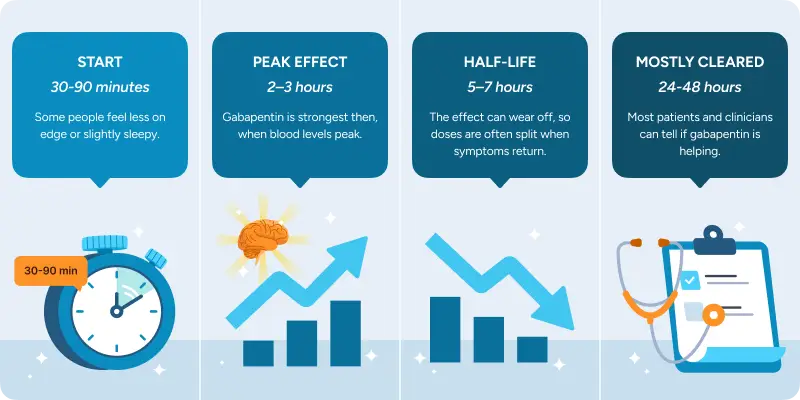
Gabapentin can start helping quickly, but the full benefit is easier to judge over the first few days. By day 2–3, it’s usually clear whether gabapentin is meaningfully helping or whether a different medication might work better.
Most people either feel a mild change after the first dose and steadier relief over the next 1–3 days, or it becomes clear that gabapentin isn’t the right fit and the plan needs to be adjusted.
Gabapentin doesn’t work the same for everyone. If the medication isn’t helping within the first couple of days, the medical team adjusts the dose or chooses a different medication option.
Most patients do not stay on gabapentin after detox. It’s usually used short-term for comfort symptoms, then tapered down or stopped before discharge once sleep, anxiety, and body symptoms settle.
Combining gabapentin with alcohol, opioids, benzodiazepines, or sleep medications can increase heavy sedation and breathing risk. This becomes dangerous if relapse happens.
There are FDA-approved medications for both alcohol and opioid cravings. Off-label options and mental health medications for co-occurring anxiety, depression, trauma, or sleep problems can also be game-changing for some patients.
The biggest safety risk with gabapentin in detox is too much sedation, especially if it’s combined with other medications or substances that also slow the brain and breathing.
The FDA also requires clinicians to:
The benefit of using Gabapentin may not outweigh the risk if:
Don’t worry if gabapentin isn’t a good fit, the medical team can use other support medications to treat the same symptoms.
Most side effects are manageable, especially when dosing is adjusted carefully. Common side effects include:
In detox, it can be hard to tell what’s a side effect versus withdrawal. In a monitored setting, the medical team tracks when symptoms start (before or after a dose) and checks alertness, breathing, blood pressure, and fall risk, then adjusts the plan.
Gabapentin is not an opioid, and it does not work like drugs that cause an intense “high.”
That said, gabapentin can be misused by some people, especially those with a history of substance use. Misuse usually means taking more than prescribed or mixing it with other sedating drugs to feel more intoxicated.
It can also cause physical dependence if it’s taken regularly for a longer time.
If gabapentin is used short-term during detox, most patients can stop without issues.
For longer durations or at higher doses, stopping suddenly can cause rebound symptoms (like anxiety or insomnia) and the recommendation is to reduce gradually over at least 1 week.
Gabapentin can be dangerous when combined with other substances that cause heavy sedation or slow breathing, including:
This is why detox teams are careful about timing after substance use, spacing doses, and monitoring. It’s also why most patients do not continue gabapentin after discharge.
For many people, the hardest part of detox is sleep loss, anxiety, and feeling physically miserable. That is where support medications like gabapentin can help, beyond the “main” detox medication.
In a medical detox, symptoms are treated, vitals are monitored, and the plan can be adjusted quickly to keep you comfortable. Plus, most insurance plans cover detox and the medications used.
Get answers about your cost / coverage now.
Your information will be kept private
Let’s talk about what’s going on — no judgment. (We’ve been there before ourselves). No one will know you inquired and there is no commitment to call.
24/7 Support
No Commitment
100% Private
There’s no catch. Checking your insurance is simply a way to see what your plan covers — it doesn’t lock you into treatment, notify anyone, or cost you anything. You get answers upfront to decide what makes sense for you.
Protecting your privacy matters! No information or notifications are ever sent to your employer or family — whether you check your insurance online or call. Everything is handled through secure, encrypted systems that meet strict medical privacy laws. You stay in control of your information!
Luckily, most insurance policies cover treatment here. Depending on the healthcare you’ve already had this year, costs could even be zero. Instead of worrying, let’s just find out what your plan covers.
Most likely. We work with major providers like Cigna, Aetna, and United Healthcare, public insurances like Tricare and tribal plans, and even smaller plans like Surest Bind and Harvard Pilgrim. The quickest way to know for sure is to check online or call. It’s a quick, private way to understand what is covered upfront.
Verifying your insurance isn’t a commitment to start treatment — it’s simply a way to see what your options are. Knowing your coverage ahead of time helps you make more informed, confident decisions. It also helps flag a spot, so you’re able to get right in if you ever do decide you’re ready.
You need your policy number to check your specific policy online. If you want general information, just call. You likely have questions beyond insurance anyway. Reaching out now helps you figure out the right fit if or when you’re ready. You don’t have to put off the call until you’re in crisis. Calling is not scary, I promise!