
Heroin is a powerful and highly addictive substance extracted from the seed pod of certain varieties of poppy plants. Heroin usage is a concerning issue worldwide, with many individuals succumbing to its addictive grip.
Despite its illegal status, heroin continues to be abused, leading to devastating consequences for individuals and their communities. Efforts to address this epidemic are ongoing, focusing on education, prevention, and treatment initiatives.
The brain is an incredibly complex organ responsible for a wide array of functions, from basic bodily processes to intricate cognitive abilities. Some of its normal functions include:
The brain controls everything we do, from thinking and feeling to moving and breathing. It’s like the command center of our bodies. Inside our brains, there are tiny structures called opioid receptors that help regulate pleasure and pain. These receptors play a big role in how people feel pleasure.
When people do something enjoyable, like eating chocolate or laughing with friends, their brains release chemicals called opioids. These chemicals bind to opioid receptors in the brain, making people feel happy and satisfied. However, when someone uses heroin, a powerful opioid, it hijacks these receptors, flooding the brain with intense pleasure.
On the flip side, when people experience pain, whether it’s from stubbing a toe or getting a paper cut, their brains also use opioid receptors to help manage it. Opioids released in response to pain can help lessen the hurt. However, with heroin use, the drug overwhelms the brain’s natural pain-relief system.
Heroin addiction is characterized by a strong need for the drug, causing severe dependency. Here is what you will learn:
Heroin is an opioid drug that exerts its effects primarily by binding to opioid receptors in the brain. The immediate effects of heroin on the brain are profound and include:
Heroin addiction often starts with heroin abuse, triggering the brain’s reward system. This leads to physical dependence, where the body relies on heroin to function. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is vital in breaking this cycle, teaching coping strategies, and addressing underlying issues driving drug use.
Long-term heroin use poses severe health risks, including brain damage. Heroin alters neurotransmitters, affecting mood and behavior. Chronic use can lead to psychological disorders like heroin use disorder. Furthermore, heroin overdose is a constant danger, highlighting the urgent need for intervention from medical professionals.
Heroin addiction can result in various psychological disorders due to its impact on the brain. These include depression, anxiety, and psychosis. Therapies are effective in addressing these issues by restructuring harmful thought patterns and behaviors.
Heroin overdose can severely damage the brain. When someone overdoses on heroin, it can slow down their breathing and heart rate, leading to a lack of oxygen in the brain. This lack of oxygen can cause brain cells to die, leading to permanent brain damage. Over time, repeated heroin use can also change the brain’s structure and function, affecting decision-making, memory, and emotions.
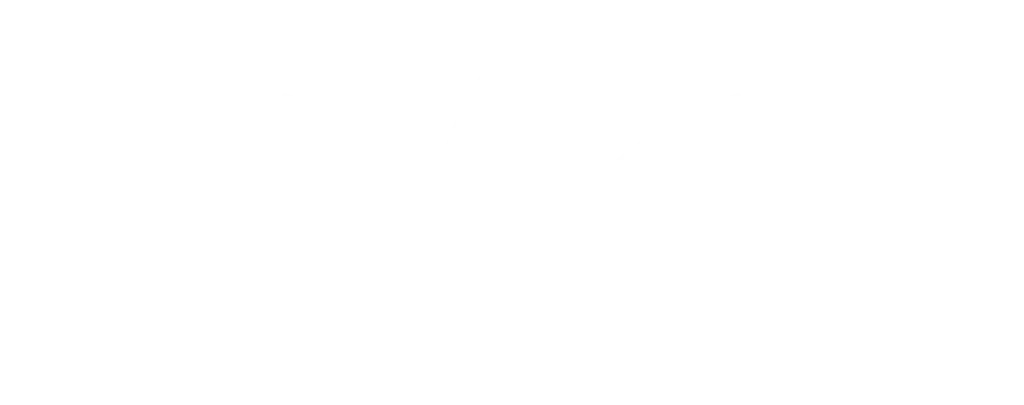
Navigating the journey to recovery can bring up many questions. Below are some of the most commonly asked questions about our services. If you need more information or have additional questions, we are only a phone call away.
How do drugs affect the brain?
Drugs can mess with how your brain works. They can change the way your brain sends messages. Some drugs can make you feel super good, but they can also mess with your judgment and decision-making. Others can make you feel relaxed or sleepy.
But abusing drugs can lead to addiction, which means your brain craves the drug, and it’s hard to stop using it. Long-term drug use can even harm your brain’s ability to think and remember stuff.
Does heroin kill brain cells?
Heroin can damage brain cells. It interferes with the brain’s communication system, disrupting the release of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that help transmit signals throughout the brain. This disruption can lead to changes in brain structure and function over time.
Chronic heroin use can impair memory, decision-making, and other cognitive abilities. Additionally, heroin overdose can cause respiratory failure, depriving the brain of oxygen and leading to permanent brain damage or death.



Boofing is a method of substance use that is not often talked about but carries

Other Categories Alcohol Use Mental Health Treatment Recovery The State of Addiction: 2025 Substance addiction
How Opioids Metabolize Opioids, when introduced into the human body, undergo a complex process of

Heroin Addiction Heroin addiction is a severe health issue in the United States. It occurs

Introduction To Heroin Teeth “Heroin teeth” refers to the severe dental damage caused by heroin

Heroin And Its Prevalence Heroin is a powerful and highly addictive substance extracted from the

Introduction To Methamphetamine Methamphetamine, often called meth, is a powerful drug that affects the brain

Meth Use Over Time: A Brief History Methamphetamine, or crystal meth, has a history marked

Meth Explained Methamphetamine, commonly known as “meth,” is a powerful synthetic central nervous system stimulant

What Does Meth Look Like Overview Of Meth Methamphetamine, commonly known as meth, belongs to

Introduction To Methamphetamines Methamphetamines, commonly known as meth or crystal meth, are highly stimulant drugs

What Is Methamphetamine Methamphetamine, or meth, is a powerful stimulant drug that belongs to the

What Is Meth? “Meth” typically refers to methamphetamine, a powerful and highly addictive central nervous

How Meth Metabolizes Methamphetamine, also referred to as crystal meth, is a strong substance that

Rise of Meth Use in The United States The prevalence of methamphetamine use is concerning,

Introduction To Ketamine Ketamine is primarily used in hospitals for pain relief and anesthesia during surgeries.

How Cocaine became what it is today Cocaine is a powerful stimulant derived from the

Benzodiazepines: An Overview Benzodiazepines, commonly known as benzos, are medications used to treat anxiety, insomnia,

Benzodiazepines Explained Benzodiazepines, commonly known as benzos, are a class of prescription medications used to

What are Benzos? Benzodiazepines, generally known as benzos, exert a calming effect on the central

Benzodiazepines are widely prescribed medications used to treat anxiety, panic disorders, seizures, and insomnia. While

Benzodiazepines: An Overview Benzodiazepines, commonly known as “benzos,” are calming to the central nervous system.


A Closer Look at Barbiturates Barbiturates, such as phenobarbital and secobarbital, are medications doctors prescribe

What are Barbiturates Barbiturates are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressants prescribed for

Suboxone, a medication commonly used for opioid addiction treatment, has shown potential benefits in managing

Suboxone, a medication primarily used to treat opioid addiction, is being explored for its potential

Other Categories Mental Health Treatment Alcohol Use Recovery Can Suboxone Help Treat Meth Addiction? Exploring

Other Categories Mental Health Treatment Alcohol Use Recovery Blue Meth: The Reality Behind the Hype

Adolescence is a critical period of brain development characterized by heightened impulsivity, risk-taking behavior, and

Other Categories Mental Health Treatment Alcohol Use Recovery What Heroin Is Cut With: Common Additives

Other Categories Mental Health Treatment Alcohol Use Recovery Suboxone, a medication used to treat opioid
Let’s talk about what’s going on — no judgement. (We’ve been there before ourselves). No one will know you inquired and there is no commitment to call.
Need someone to talk to? We’re always here—day or night.
Ask questions, get guidance—no pressure, no obligation.
Your story stays with us. Confidential support, always.
Copyright © 2025 The Haven Detox. All rights reserved